Table of contents
- What is Git?
- What is Github?
- What is Version Control? How many types of version controls do we have?
- Why do we use distributed version control over centralized version control?
- Create a new repository on GitHub and clone it to your local machine.
- Make some changes to a file in the repository and commit them to the repository using Git.
- Push the changes back to the repository on GitHub
What is Git?
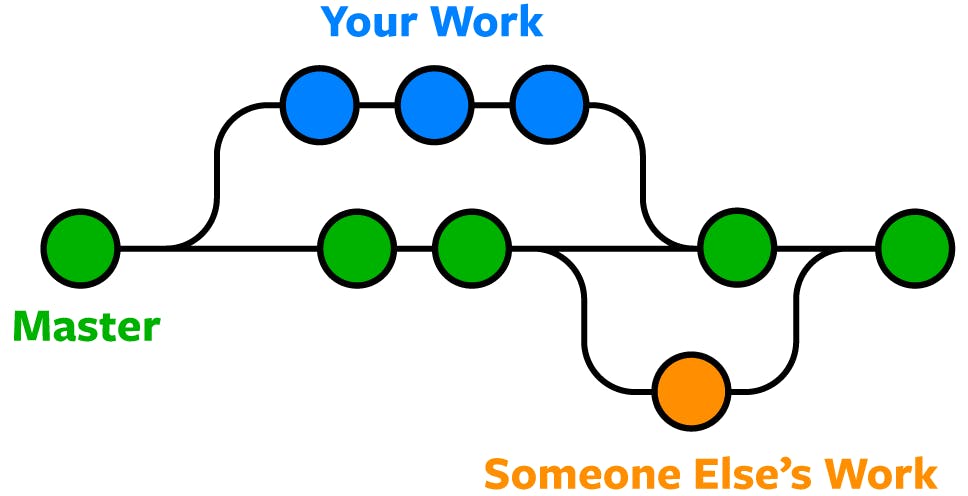
Git is a version control system that allows you to track changes to files and coordinate work on those files among multiple people. It is commonly used for software development, but it can be used to track changes to any set of files.
With Git, you can keep a record of who made changes to what part of a file, and you can revert back to earlier versions of the file if needed. Git also makes it easy to collaborate with others, as you can share changes and merge the changes made by different people into a single version of a file.
What is Github?
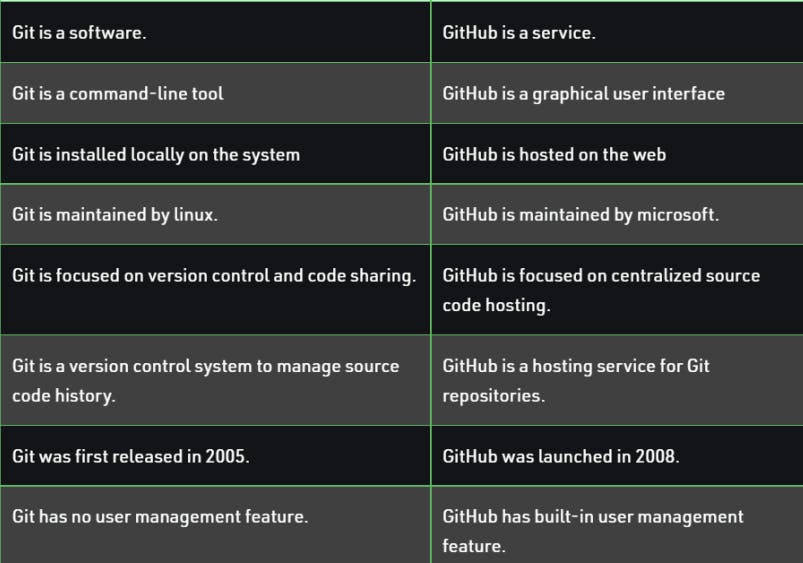
GitHub is a web-based hosting service for version control using Git. It provides a platform for developers to store, manage, and share their code repositories with others. GitHub is widely used by individual developers, open-source projects, and large organizations.
What is Version Control? How many types of version controls do we have?
Version control is a system that tracks changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. It allows you to revert files back to a previous state, revert the entire project back to a previous state, compare changes over time, see who last modified something that might be causing a problem, who introduced an issue and when, and more.
There are two main types of version control systems
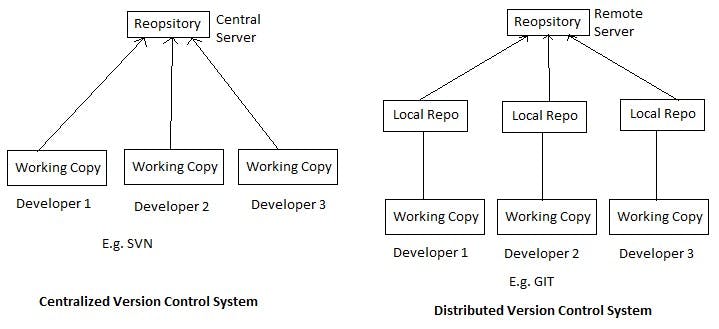
Centralized Version Control System (CVCS) uses a central server to store all the versions of a project's files. Developers "check out" files from the central server, make changes, and then "check in" the updated files. Examples of CVCS include Subversion and Perforce.
Distributed Version Control System (DVCS) allows developers to "clone" an entire repository, including the entire version history of the project. This means that they have a complete local copy of the repository, including all branches and past versions. Developers can work independently and then later merge their changes back into the main repository. Examples of DVCS include Git, Mercurial, and Darcs.
Why do we use distributed version control over centralized version control?
Better collaboration: In a DVCS, every developer has a full copy of the repository, including the entire history of all changes. This makes it easier for developers to work together, as they don't have to constantly communicate with a central server to commit their changes or to see the changes made by others.
Improved speed: Because developers have a local copy of the repository, they can commit their changes and perform other version control actions faster, as they don't have to communicate with a central server.
Greater flexibility: With a DVCS, developers can work offline and commit their changes later when they do have an internet connection. They can also choose to share their changes with only a subset of the team, rather than pushing all of their changes to a central server.
Enhanced security: In a DVCS, the repository history is stored on multiple servers and computers, which makes it more resistant to data loss. If the central server in a CVCS goes down or the repository becomes corrupted, it can be difficult to recover the lost data.
Create a new repository on GitHub and clone it to your local machine.
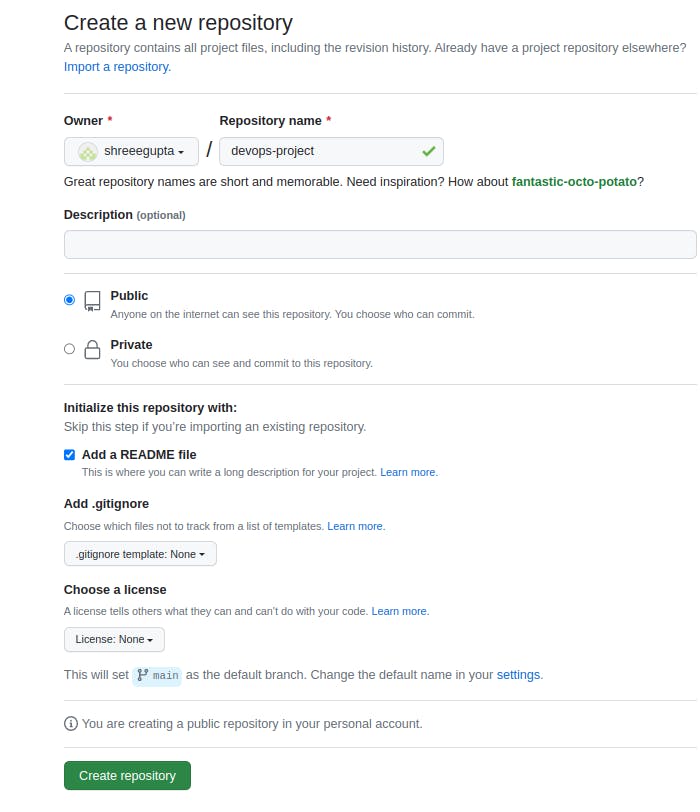
- Log in to your GitHub account and click on the New button to create a new repository. Enter a name for your repository and choose whether the repository should be public or private.
- Once the repository is created, copy the repository's URL to your clipboard.
Open up a terminal or command prompt on your local machine and navigate to the directory where you want to clone the repository.
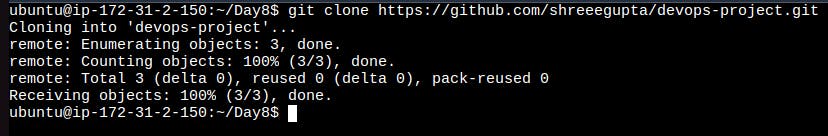
Now clone the repository by using this command.
git clonehttps://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/YOUR-REPOSITORY
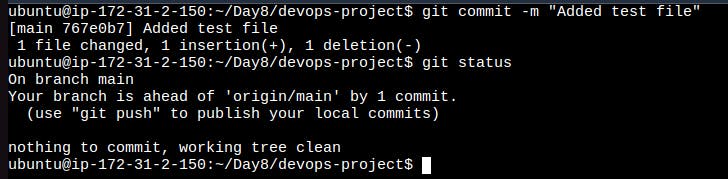
Make some changes to a file in the repository and commit them to the repository using Git.
Create a test file using vim editor and check status using this command, it'll show untracked file.
git status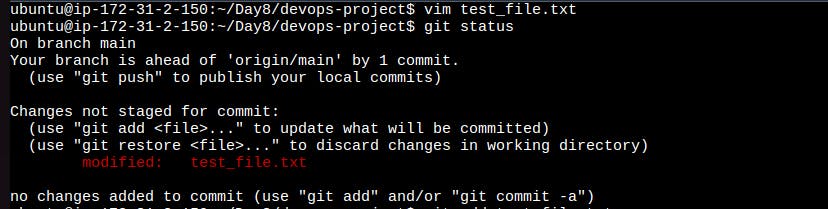
Add the test file to the staged area and check status, now it's tracked.
git add .Orgit add FILENAME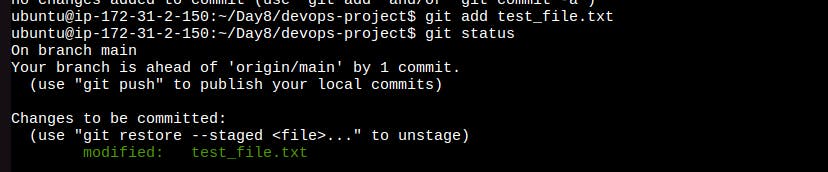
Commit staged file to the git using this command.
git commit -m "Your Message"
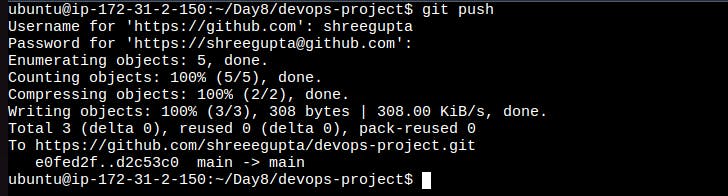
Push the changes back to the repository on GitHub
The git push command is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository.
git push <remote> <branch>
Thank you for reading!!
~Shreya Gupta
Great initiative by the #trainwithshubham community. Thank you Shubham Londhe
#devops #90daysofdevops #linux #git #github
