What is ECS?
ECS (Elastic Container Service) is a fully-managed container orchestration service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows you to run and manage Docker containers on a cluster of virtual machines (EC2 instances) without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
With ECS, you can easily deploy, manage, and scale your containerized applications using the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or the API. ECS supports both "Fargate" and "EC2 launch types", which means you can run your containers on AWS-managed infrastructure or your own EC2 instances.
ECS also integrates with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing, Auto Scaling, and Amazon VPC, allowing you to build scalable and highly available applications. Additionally, ECS has support for Docker Compose and Kubernetes, making it easy to adopt existing container workflows.
Overall, ECS is a powerful and flexible container orchestration service that can help simplify the deployment and management of containerized applications in AWS.
Difference between EKS and ECS?
EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) and ECS (Elastic Container Service) are both container orchestration platforms provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). While both platforms allow you to run containerized applications in the AWS cloud, there are some differences between the two.
Architecture: ECS is based on a centralized architecture, where there is a control plane that manages the scheduling of containers on EC2 instances. On the other hand, EKS is based on a distributed architecture, where the Kubernetes control plane is distributed across multiple EC2 instances.
Kubernetes Support: EKS is a fully managed Kubernetes service, meaning that it supports Kubernetes natively and allows you to run your Kubernetes workloads on AWS without having to manage the Kubernetes control plane. ECS, on the other hand, has its own orchestration engine and does not support Kubernetes natively.
Scaling: EKS is designed to automatically scale your Kubernetes cluster based on demand, whereas ECS requires you to configure scaling policies for your tasks and services.
Flexibility: EKS provides more flexibility than ECS in terms of container orchestration, as it allows you to customize and configure Kubernetes to meet your specific requirements. ECS is more restrictive in terms of the options available for container orchestration.
Community: Kubernetes has a large and active open-source community, which means that EKS benefits from a wide range of community-driven development and support. ECS, on the other hand, has a smaller community and is largely driven by AWS itself.
In summary, EKS is a good choice if you want to use Kubernetes to manage your containerized workloads on AWS, while ECS is a good choice if you want a simpler, more managed platform for running your containerized applications.
Set up ECS (Elastic Container Service) by setting up Nginx on ECS.
Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to the ECS service and click on "Create Cluster"
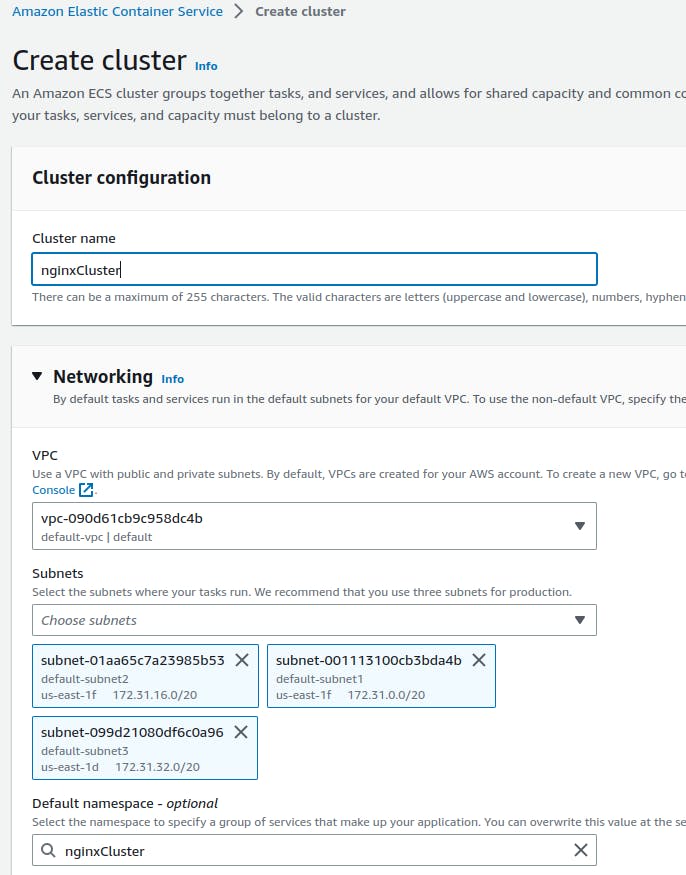
Configure the cluster details, such as cluster name, instance type (for EC2), and VPC settings.
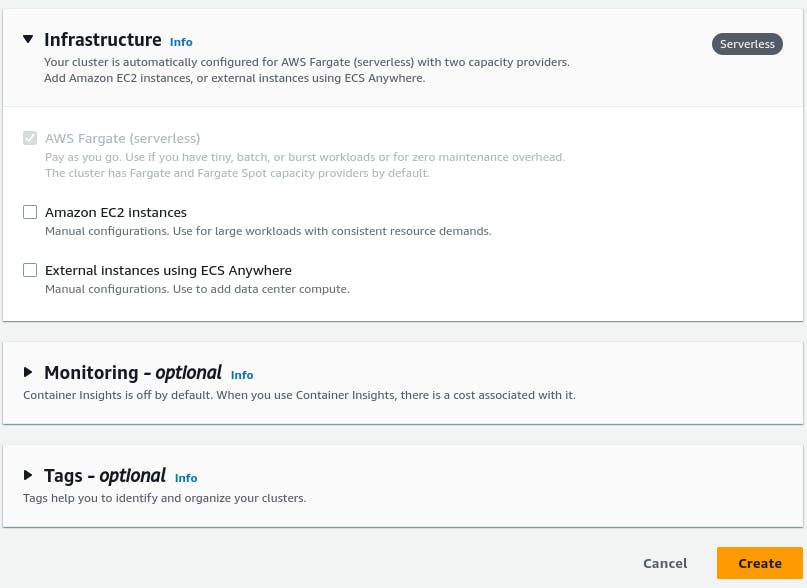
Review the configuration and create the cluster.
In the ECS console, click on "Task Definitions" in the sidebar and then "Create new Task Definition."
Go to the public Elastic Container Repository(ECR) gallery.ecr.aws to copy the NGINX image URL.
Choose a task definition name and specify the container configuration.
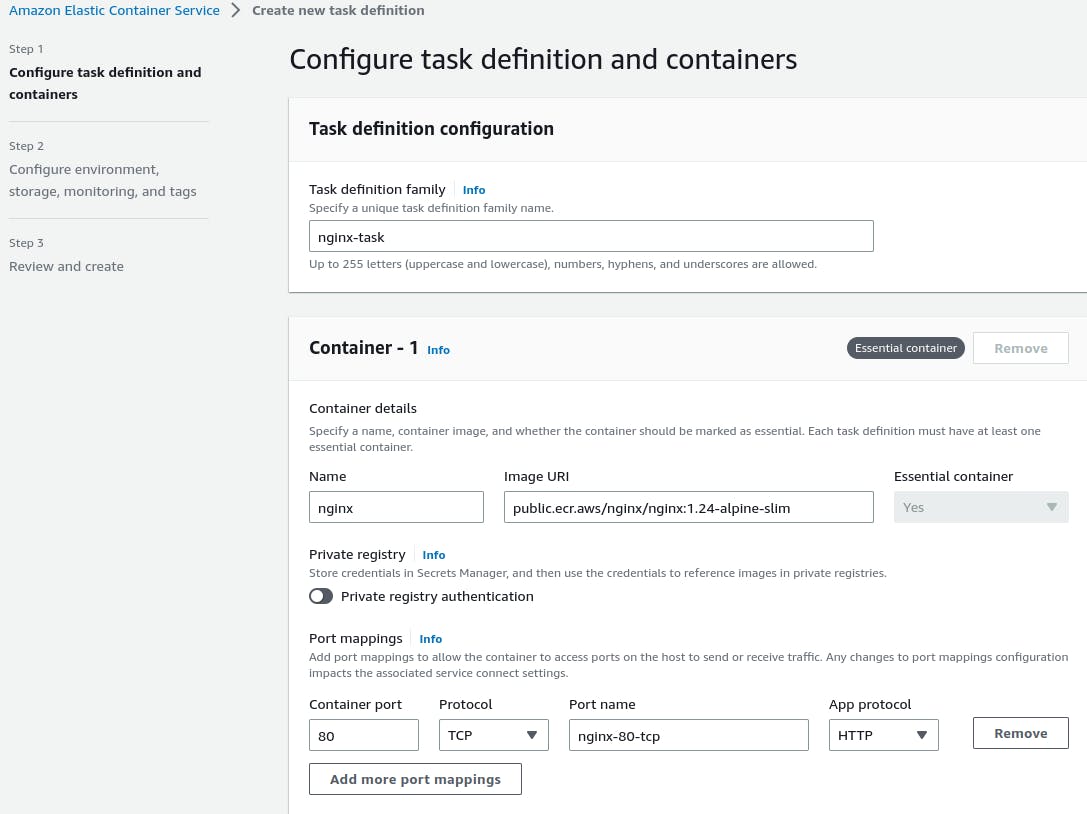
For Nginx, provide the container image, memory and CPU limits, port mappings, and any environment variables.
Configure additional settings like logging, networking, and IAM role. Review the task definition and create it.
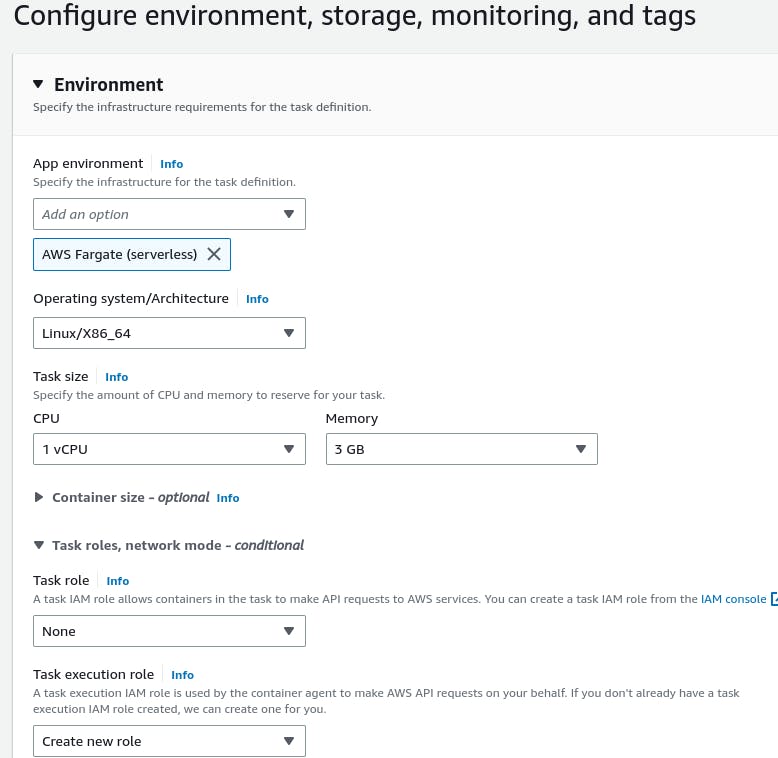
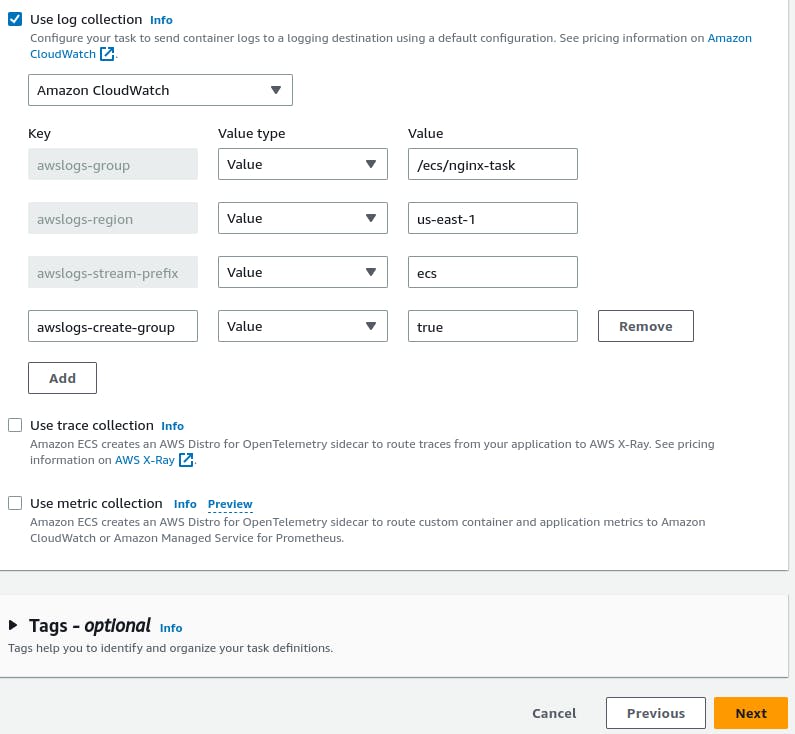
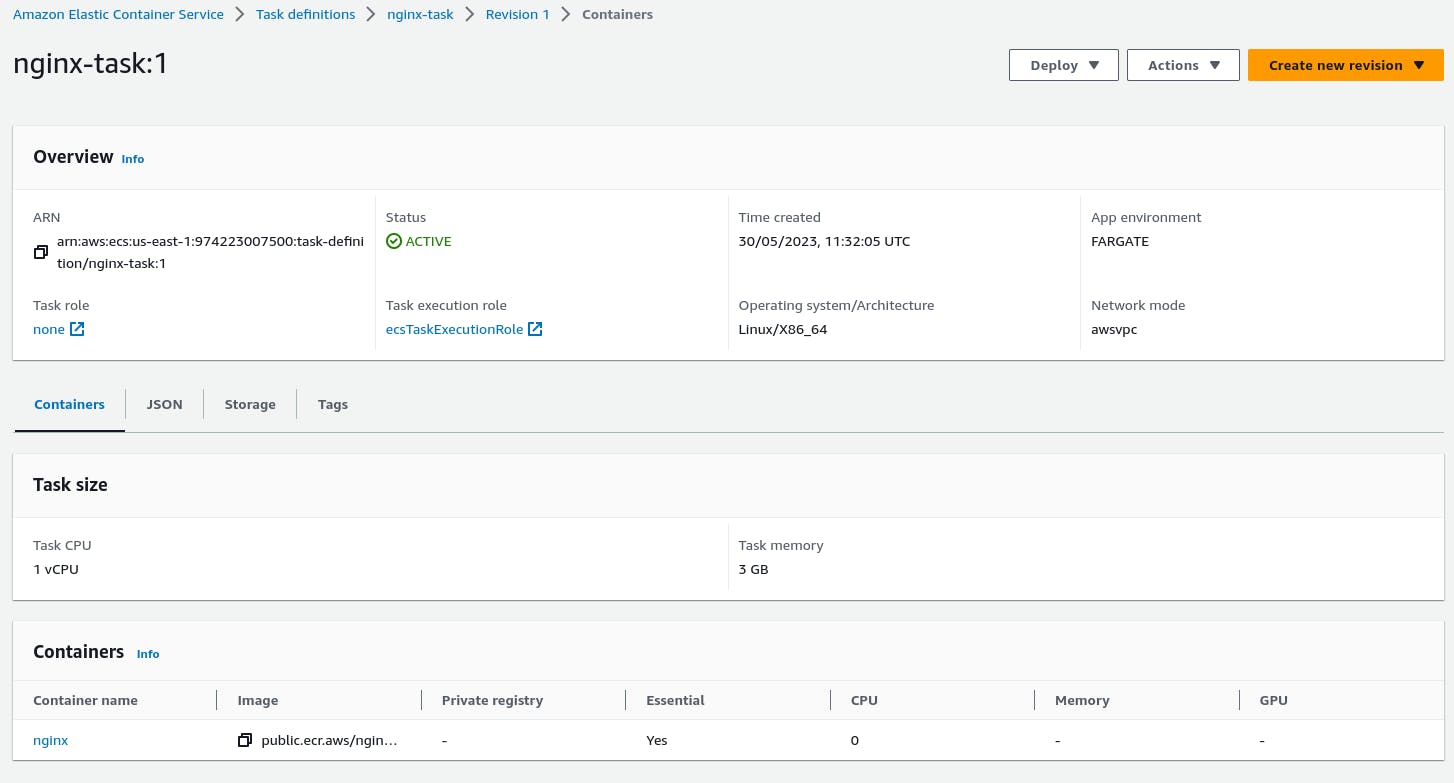
A task is created.
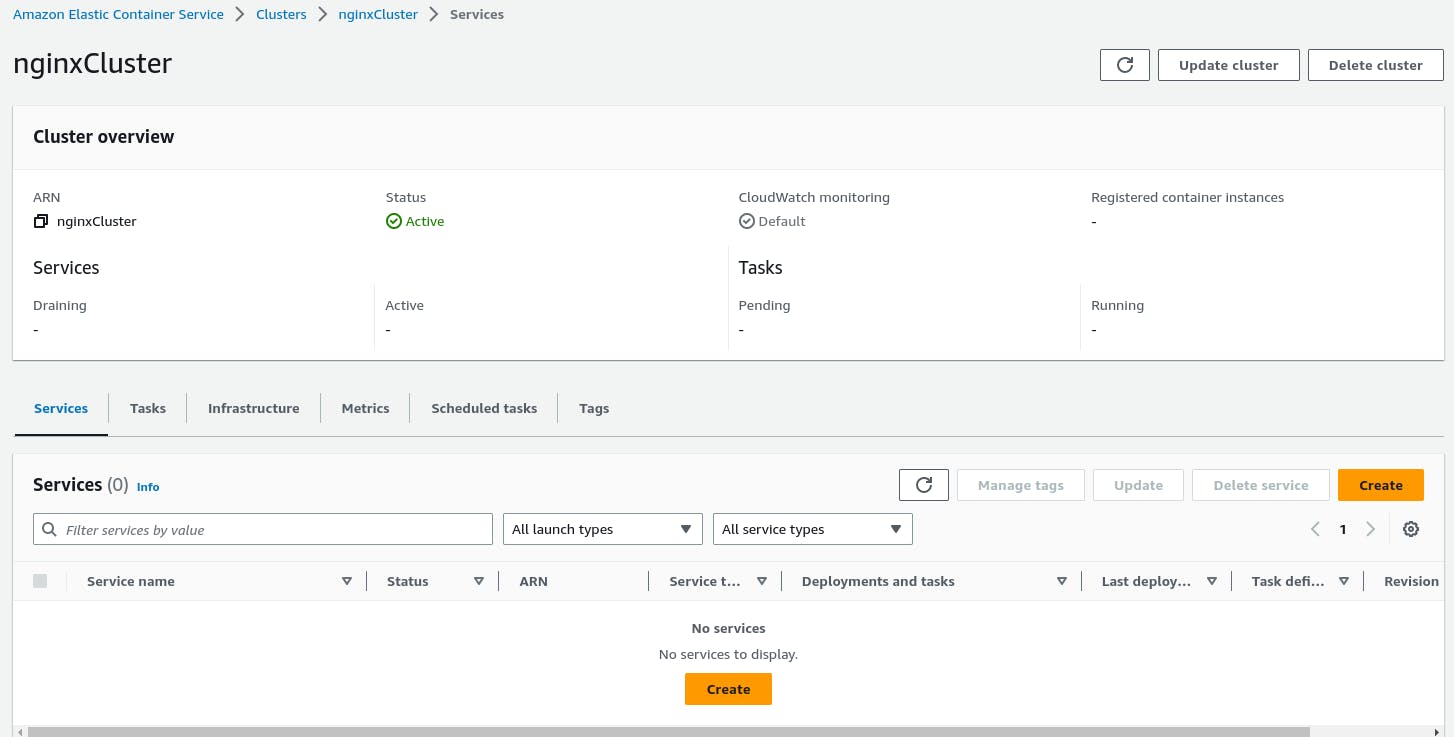
In the ECS console, select your cluster and click on "Create" in the Services tab.
Choose a launch type (EC2 or Fargate) and select the task definition created in the previous step.
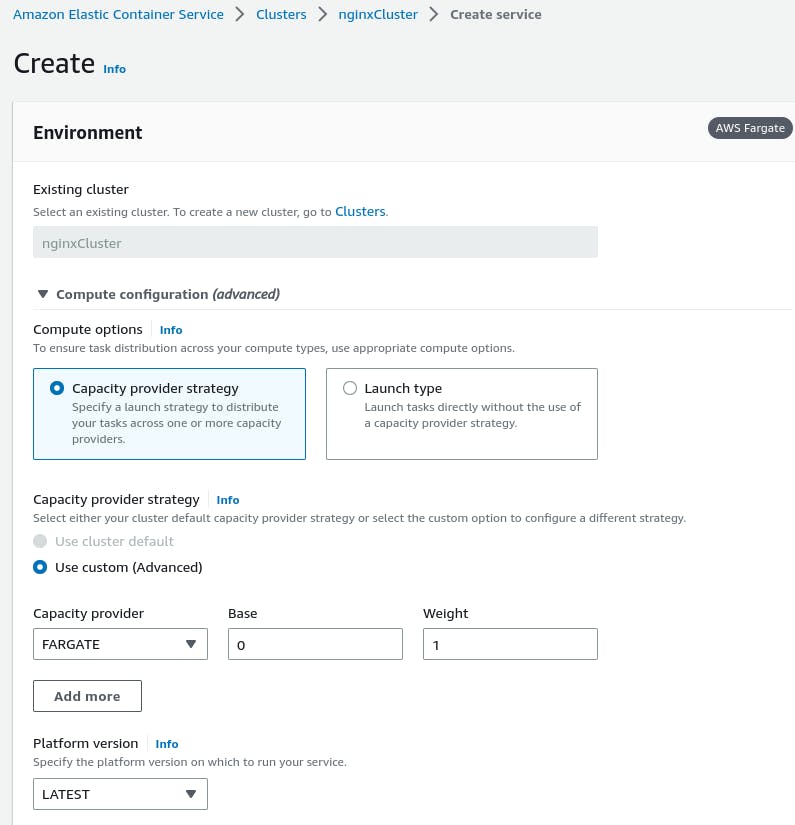
Configure the service details, such as service name, desired tasks, network settings, and load balancing.
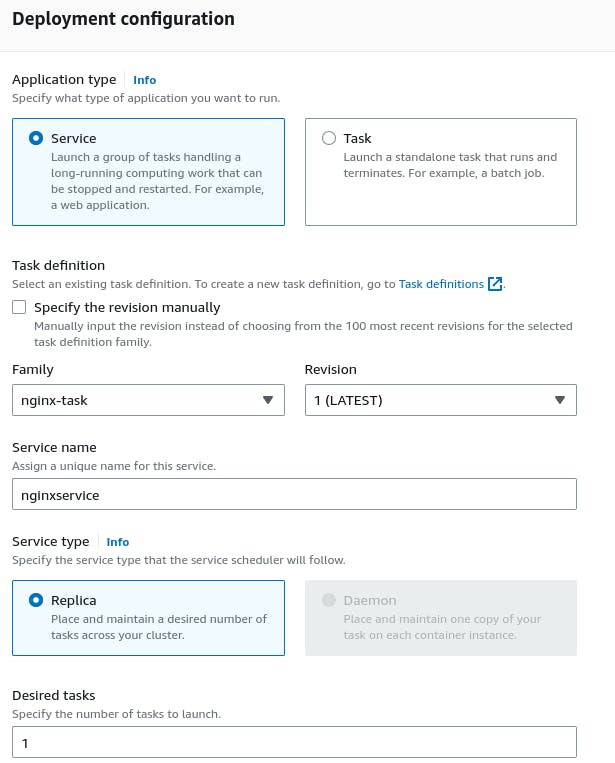
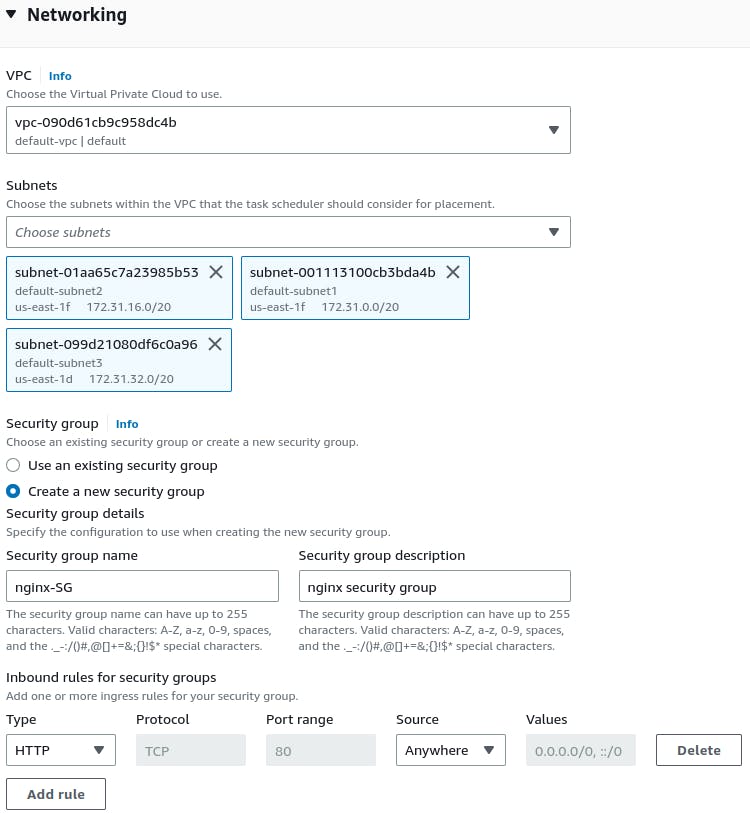
Review the service configuration and create it.
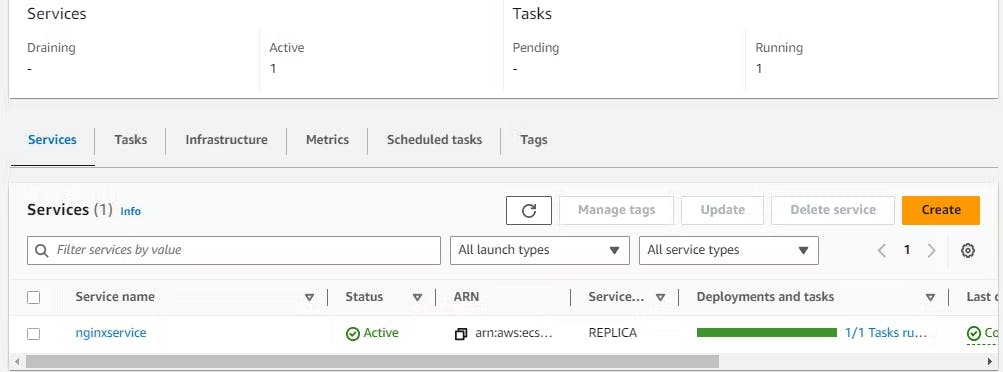
Click on the 'Cluster' that you created.
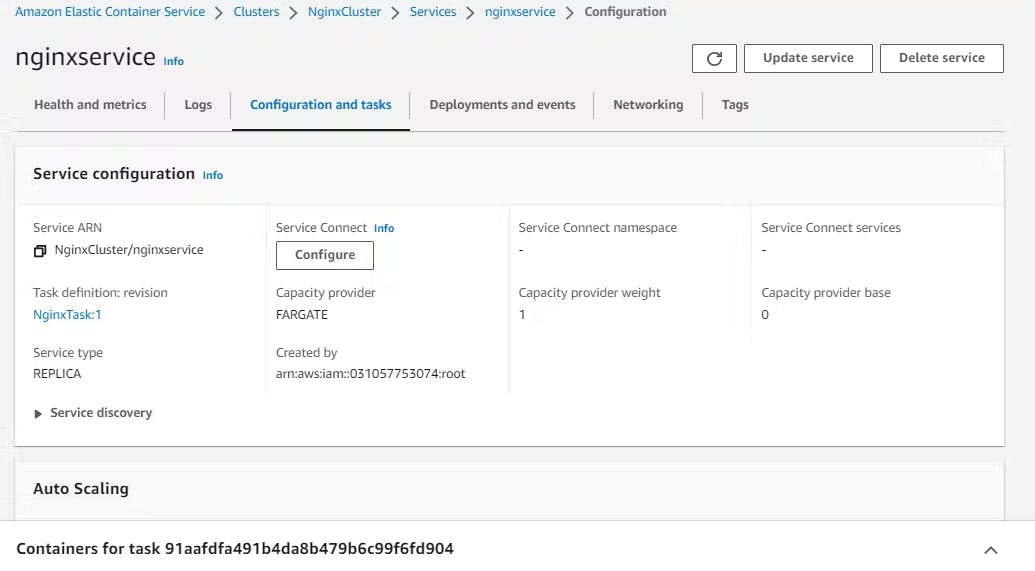
Click on 'Task' and go to the 'Configuration' section, there you can see public IP.
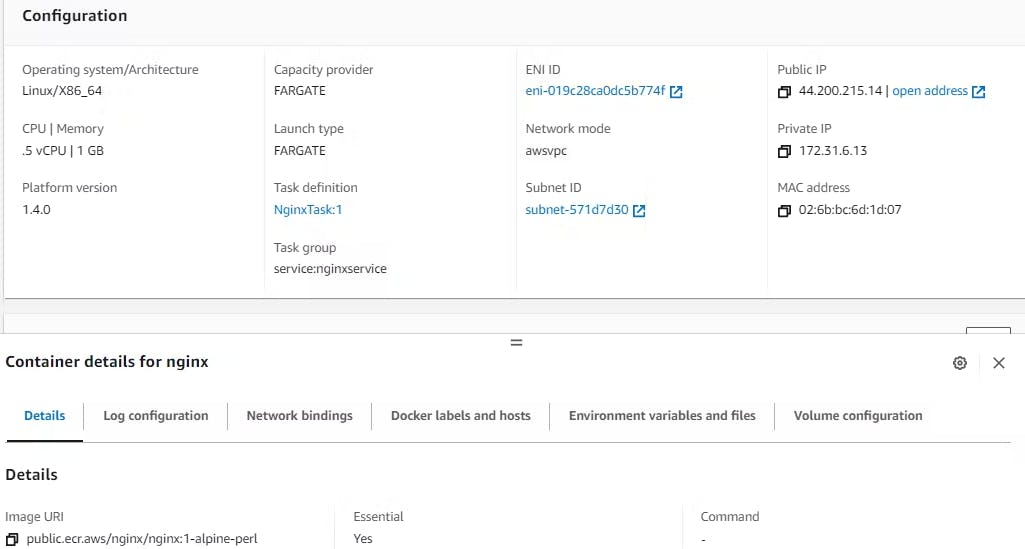
Copy the Public Ip to access the URL.
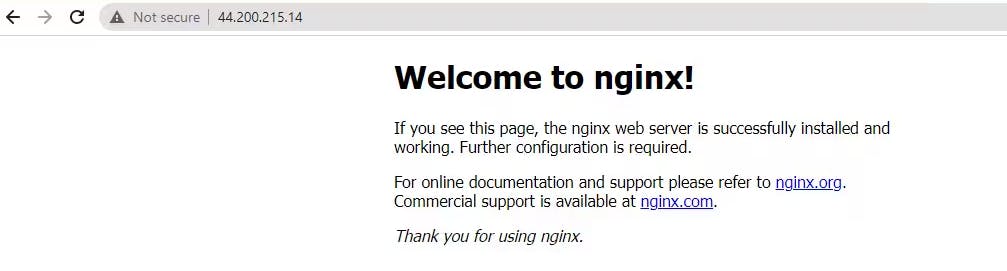
That's it! We've successfully set up ECS and deployed Nginx on ECS. We can now scale and manage your Nginx containers using the ECS service.
Thank you for reading!!
~Shreya Gupta
Great initiative by the #trainwithshubham community. Thank you Shubham Londhe
#devops #90daysofdevops #aws #iam #ecs

